|
L4 CSL - CONSORZIO SICILIANO LEGALLINEFELICI (IT) |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
FUNCTIONS APPLIED TO THE LAND |
|||||
|
ECONOMIC |
|||||
|
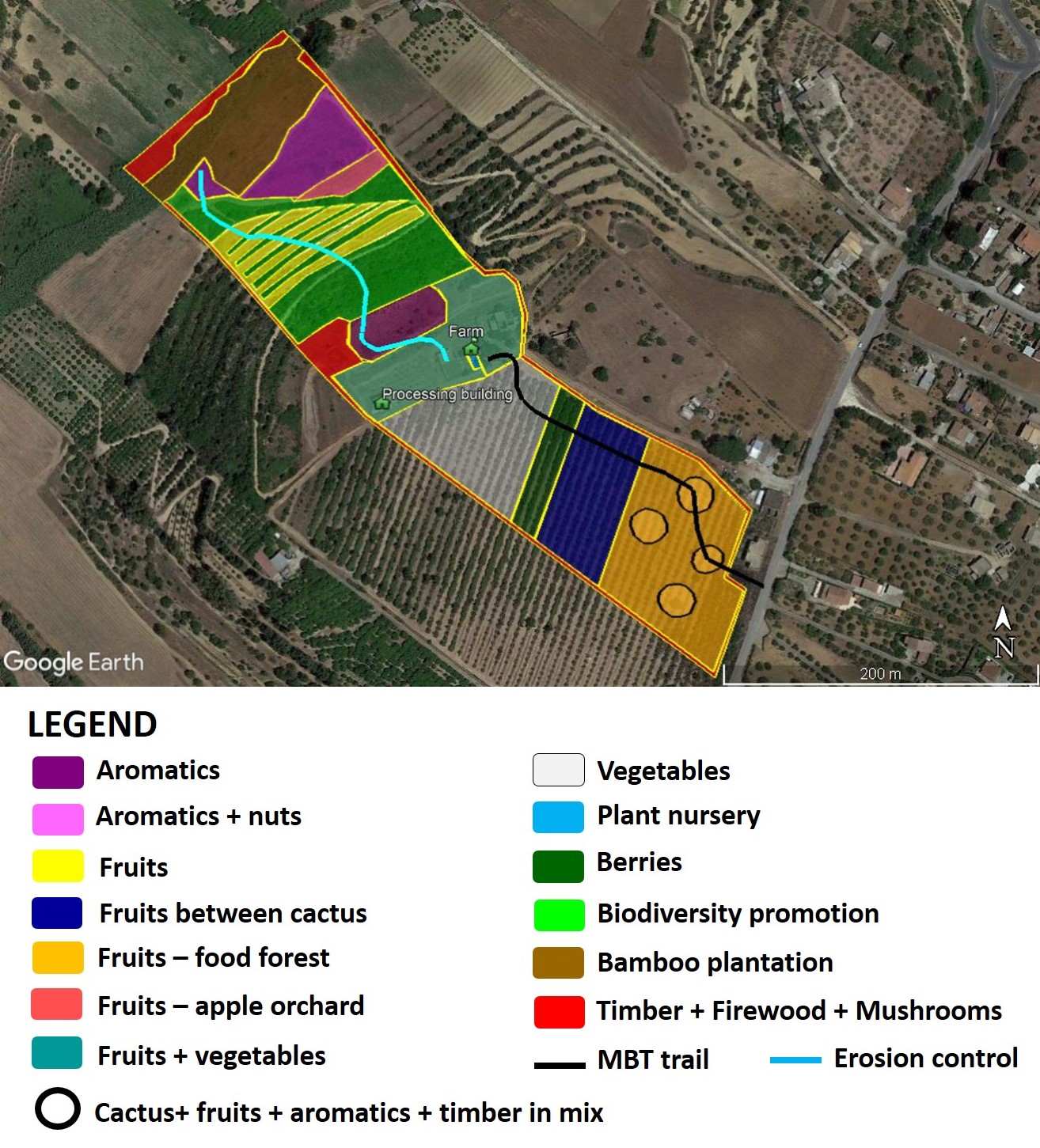
Aromatics [1] |
A crater garden with several aromatics (e.g. oregano, lavender, rosemary, sage). Wild picking. Marketing in collaboration with consortium partners. | ||||
|
Aromatics + nuts [1, 15] |
Almond trees will be planted with aromatics. | ||||
|
Fruits [7] |
Most fruit trees are already planted. Some interplanting can take place. | ||||
|
Fruits interplanted with cactus [7] |
Fruits, such as pomegranate and wild apple, are interplanted with cactus. Furthermore, grass strips between cactus rows are improved for pollinators. | ||||
|
Food forest [7, 1, 19, 46] |
It is a food forest between cactus, with circular areas dedicated to aromatics and timber species in a mix. Several species were selected: avocado, quince, pomegranate, almond, etc. | ||||
|
Apple orchard [7] |
Existing apple production. Adding wild apple trees. There is a good local market for apples. | ||||
|
Fruits and vegetables [7, 10] |
Around the farm, small quantities of special species such as Actinidia chinensis, are combinated with fresh vegetables. | ||||
|
Vegetable between cactus rows [10] |
Various vegetable species are selected year-by-year, depending on market. | ||||
|
Bee keeping [11] |
Currently bee keeping is entrusted to a thirdy party. honey production is not significant.
|
||||
|
Mushrooms [12] |
Mulching creates the optimal soil condition for the natural growth of edible mushrooms. | ||||
|
Natural fibres [13] |
Fibre is extracted from the cactus. the university of palermo made a study. a Market research is needed to identify companies that might be interested to use this material and test it. | ||||
|
Plant nursery [14] |
A small nursery was started. | ||||
|
Berries [18] |
Small-scale blackberry production. | ||||
|
Bamboo plantation [19] |
Existing bamboo plantation. | ||||
|
Timber and firewood [19, 12, 39,40, 46] |
The idea is the creation of a natural fence 3 meters wide (Europ nettle tree, figs, Rhamnus alaternus). Quercus trees will be inoculated with mi mychorrizae for mushrooms. New fence to be repaired or constructed for as long as the natural fence is not full grown. Currently sprouts are also used as planting sticks and fencing poles. |
||||
|
ECOSERVICES |
|||||
|
Food self-sufficiency [24] |
The idea is the creation of a network of 200 families that will order their required stuff once a year. | ||||
|
MTB trail [28] |
Creation of a ‘MTB café’ where bikers drink something and buy local products. |
||||
|
Test Area [32] |
Testing: i) Opuntia leaves as mulching, chips in different mix; ii) mobile henhouses. |
||||
|
Study & Research Facilities [34] |
The farm will be an experimental and test area for organic and regenerative techniques. landowner offers area for research execution to universities, associations, NGO’s, other landowners. Volunteers are already hosted. |
||||
|
Study and guided tour [35] |
Landowner already works with schools. | ||||
|
ENVIRONMENTAL |
|||||
|
Erosion control + timber [37, 19, 45] |
To limit and reduce surface soil erosion, rain pipes were built to collect excess rainwater in the terraces of the crater garden, and in the contour lines of almond grove and the orchards. | ||||
|
Wildlife protection [39] |
Bird and bat houses, as well as insect hotels installed to increase biodiversity of beneficial organisms like pollinators and natural enemies of pest. Poles for raptors. Furthermore, shelter for hedgehog and weasel were installed. | ||||
|
Insect and bird shelter [40] |
|||||
|
Biodiversity promoting plants [46] |
Natural fences around the property support biodiversity and in the meantime act as firebreak lines. |
||||
|
SOCIAL |
|||||
|
Create employment [47] |
When production increases, employment will follow. | ||||
|
Provide social services [49] |
Working with schools. | ||||
|
Working with migrants [50] |
Landowner already works with migrants. | ||||
| MEASURES APPLIED TO THE LAND | |||||
| N. | Name | Comments | |||
| 1 | Seed collecting & native species |
Sicilian forestry protocol establish seedlings must be produced with seeds collected locally. |
|||
| 3 | Existing vegetation |
Natural regeneration is the focus in several areas. Oak, hawthorn, almond tree, and hackberry were left inside the preakly pear orchard , as well as some blackberry brushes. |
|||
| 4 | Mycorrhizae & plants |
Mycorrhizae used to produce mushrooms and inoculated onto plants to make them more resilient to droughts, diseases and increases root surface. This in cooperation with University of Palermo. |
|||
| 9 | Half-moons |
On slopes. |
|||
| 11 | Conservation Tillage |
Everywhere no tillage for this property. |
|||
| 14 | Organic fertilizer |
Mainly own prickly pear residuals. The "pastazzo" citrus waste-derived compost produced in Sicily was also added to soil. |
|||
| 23 | Planting in mixes |
Everywhere planting in mixes. |
|||
| 26 | Plant support Water aids study |
Prickly pear residuals (fresh or dried crushed cladodes, or fresh in the bottom of the planting hole) and juta coffee bags are been used, as well as wheat straw in the almond grove. Cocoons were installed. |
|||
| 27 | Watering/Drip irrigation | Tube with drip irrigation or manual emergency irrigation where needed. | |||
| 29 | Plant assist |
Prickly pear residuals (integer and crushed cladodes) and juta coffee bags and wheat straw. |
|||
| 31 | Grafting trees |
Trees grafted in both nursery (apple, pomegranate and avocado) and in the field (wild olive and almond, quince). |
|||
| 32 | Diseased trees |
First an analysis of potential death causes. If diseases, seedlings/plants are removed then buried, crushed or burned. |
|||
| 33 | Weed control |
No chemicals. Mulching and cutting. |
|||
| 34 | IPM Plague control |
By now no plagues, but if needed IPM will be used. |
|||
| 35 | Prunings |
Pruning will be used as mulching, compost or chipped. |
|||
| 43 | Planting on ridges? |
Yes, planting in furrows in crater gaden. |
|||
| 44 | Firewood 10% rule |
Most deadwood is chipped, but perhaps some can be left. |
|||
| 52 | Root protection |
Light Machines are used only to superficially till areas. |
|||
| Numbers of functions and measures correspond to the list reported in the DAM methodology, defining the operative DAM plan
http://www.desert-adapt.it/index.php/en/case-studies/dam-methodology |
|||||
| FIELD IMPLEMENTATION OF THE DAM PLAN | |||||
|
Testing plant growth aid techniques to support seedlings establishment and growth [Adaptation Measures: plant support & water aid 26 - plant protectors 28 - plant assist 29] Michele Russo, project manager of CSL (L4) tested the DAM in the Caudarella farm experimenting nature based solutions for soil improvement. Residues of the cladodes of prickly pear plants cultivated in the farm (Pict. 1) were used as mulching material at site and to grow a vegetal orchard (Pict. 2). Cladode significantly increase the soil water retention capacity and provide organic matter and nutrients. Picture 3 shows the remaining moisture content of soil after a raining event occurred 20 days before. The landowner used prickly pear pruning to prepare the soil before planting berries (Pict. 4-5). In addition to prickly pear residuals the "pastazzo" citrus waste-derived compost (Pict. 6) was used as organic soil amendment. Other low cost mulching materials were tested and compared: biodegradable juta bags (Pict. 7) and wheat straw (Pict. 8-9). |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Fruit nuts and vegetables [Economic Functions: Fruits 7;Vegetables 10; Nuts 15] New fruit trees were planted to improve the existing fruit production such as apples, almond and figs. Wild and local species were selected because more adapted to soil and climate local conditions. Almond and fig were planted in single hole digging and following contour lines (key lines design, Pict.1). Prickly pear cladodes were placed at the bottom and raw wheat straw and residuals of fungi cultivation were used as mulching (Pict. 2-3). A food forest was crated inter planting fruit trees between existing cactus raws (pict. 4, 5 avocado). Pict. 6 and 7 show drip irrigation installed in the vegetable area. To maintain cleaned the farm and reduce the fire risk, landowner is testing mobile henhouses (Pict. 8). |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Actions to increase local biodiversity [Adaptation Measure: insect shelters 40] As part of the measures to increase the local biodiversity it is important to offer a niche or house to host birds and bats in agricultural areas. Both bats and birds have key ecological functions useful to control pest, being their natural enemies, and to increase greening and plant germination via diffusion of the seeds. L4 is implementing these hosting facilities in its land (Pict. 1-2) Measures to favor biodiversity in each sites included the set up of bird houses and insect hotels. Bird houses were already set while insect hotels will be provided by a collaboration with local schools. |
|||||
|
|
|||||
|
Meteo station A meteo station was placed in the site as part of the project monitoring activity. The meteo records the rainfall and the main meteorological data. The data analysis might allow to define the fine scale metereological trend of the area in the 5 years of the project to be compared with downscaling analysis of the site provided by the scientific team. |
|||||
|
|
|||||
| |
|||||
|
Crater garden [Economic Functions: aromatics 1 and fruits 7; Environmental function: erosion control 37; Adaptation Measure: Organic fertilizer 14, regular planting 24, planting on ridges 43] A crater garden was created in place of an earth dam which was never used (Pict.1). The field actions involved a complete reorganization of the area. The profile of the original crater was reshaped creating small terraces, which reduced erosion, enhancing the capacity of the soil to collect rainfall reducing run-off (Pict. 2). Chestnut poles were used to create the terrace like systems (Pict. 3-7). The terraces were planted with aromatic shrubs and small fruit trees, which helped in stabilizing soil structure and reducing soil loss risk. A water channel collecting rainfall (Pict. 8) is used for capillary irrigation of plants. The "pastazzo", a residual of citrus processing, was used as organic fertilizer. Furthermore, a small artificial pond will be created in the lower part of crater garden to improve biodiversity. |
|||||
|
|
|||||